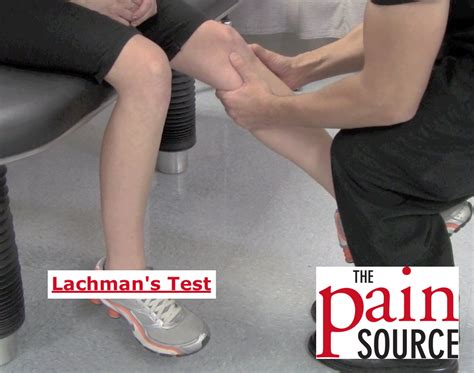
lachman compression test|lachman test for knees : trading Lachman test: flex the knee only 20-30 degrees (rather than 90 degrees in anterior drawer sign), then attempt to pull tibia anterior relative to the femur. If positive, a deficient ACL will demonstrate increase movement forward.
webJogue o caça-níqueis Zeus da WMS apenas para se divertir. Leia nossa análise, deixe uma avaliação e conheça os melhores bônus de depósito, ofertas de rodadas grátis e bônus .
{plog:ftitle_list}
5 dias atrás · The (Galician) gaita or gaita de foles is a traditional bagpipe used in Galicia, and Portugal. The name gaita is used in Galician, Spanish, Leonese and Portuguese as a generic term for "bagpipe". Just like "Northumbrian smallpipe"' or "Great Highland Bagpipe", each country and region attributes.
Diagnosis can be suspected clinically with presence of a traumatic knee effusion with increased laxity on Lachman's test but requires MRI studies to confirm diagnosis. Treatment involves ligamentous reconstruction utilizing a variety of techniques and graft choices .posterolateral drawer test performed with the hip flexed 45°, knee flexed 80°, and .The Lachman test is a passive accessory movement test of the knee performed to identify the integrity of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). The test is designed to assess single and sagittal plane instability.The Lachman test is the most accurate test for detecting an ACL tear. Magnetic reso-nance imaging is the primary study used to diagnose ACL injury in the United States. It can also.
The Lachman test is a specific clinical exam technique used to evaluate patients with a suspected anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) injury. The test relies on proper positioning .Lachman test: flex the knee only 20-30 degrees (rather than 90 degrees in anterior drawer sign), then attempt to pull tibia anterior relative to the femur. If positive, a deficient ACL will demonstrate increase movement forward. A positive Lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, and a negative Lachman test is fairly good evidence against .Lachman Test. Purpose: To assess the integrity of the ACL. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The patient should be relaxed for this test, especially the tested extremity. The .
There is a definite loss of passive range of motion., Running, jogging, and sprinting are examples of A. function tests B. the Lachman's test C. varus stress test D. the Apley's compression test, Which of the following is the bursa that commonly becomes inflamed from the overuse of the patellar tendon? Dan Smith, DO performs the Lachman Test on a patient as part of a full knee exam Lateral Patellar Compression Syndrome . Lachman's test. most sensitive exam test. grading. A= firm endpoint, B= no endpoint. Grade 1: 5 mm translation. Grade 2 A/B: 5-10mm translation. Grade 3 A/B: >10mm .Introduction [edit | edit source]. Meniscus tears are the most common injury of the knee. Medial meniscus tears are generally seen more frequently than tears of the lateral meniscus, with a ratio of approximately 2:1. Meniscal tears may occur in acute knee injuries in younger patients or as part of a degenerative process in older individuals.
Test Movement. From the starting position the examiner pulls anteriorly on the proximal tibia. Positive Lachman Test. This test is considered positive if there is a soft or mushy end feel to the translation of the tibia. A soft end feel / endpoint is indicative of secondary structures stopping the continued anterior translation of the tibia . The Apley grind test, also known as the Apley compression test or the Apley test, is a maneuver performed to evaluate meniscus injury. Clinicians usually perform it in conjunction with the Apley distraction test, which assesses for ligamentous injury. Meniscal injuries are very common and are associated with significant pain and morbidity.If the patient can complete and maintain the contraction without pain, the test is considered negative. If the test causes Retropatellar Pain and the patient cannot maintain the contraction without pain, the test is considered positive. Precaution [edit | edit source] The amount of pressure applied must be carefully controlled as more pressure can elicit positive response .
Your provider will physically move your leg and knee joint to identify any pain or other symptoms you feel during the movements. The McMurray test is usually part of a preliminary exam when you visit your provider with knee pain or after an injury. You’ll probably also need at least one of a few imaging tests to confirm a torn meniscus or any other injuries in your knee.
lachman test reviews
The Lachman test is the test of choice for the acutely injured knee. The reasons for this are: An acute injury with an associated haemarthrosis prevents knee flexion to 90 degrees; . Any “popping” or pain along the joint line is considered .Noble Compression Test. Purpose: To assess for iliotibial band friction syndrome. Test Position: Supine. Performing the Test: The affected limb's hip and knee are passively flexed to 90 degrees. The examiner applies pressure with the thumb over the IT Band proximal to the lateral femoral condyle. The patient then actively extends the hip and knee. Better tests are the Lachman test and the pivot-shift test , which have reported respective sensitivities of 0.87 and 0.49 and specificities of 0.97 and 0.98. 7 The pivot-shift test is a dynamic .
Pain during compression and rotation suggests a meniscal injury; pain during distraction and rotation suggests a ligamentous or joint capsule injury. For evaluation of the medial and lateral collateral ligaments, the patient is supine, . The Lachman test is the most sensitive physical test for acute anterior cruciate ligament tears (2). Enroll in our online course: http://bit.ly/PTMSK DOWNLOAD OUR APP:📱 iPhone/iPad: https://goo.gl/eUuF7w🤖 Android: https://goo.gl/3NKzJX GET OUR ASSESSMENT B.Active Lachman Test . Knee Orthopedic Exam Test. . A positive test is noted by watching the lateral aspect of the knee to see if the lateral tibial plateau will gently subluxate or slide forward on the femoral condyle as extension is initiated (relative to the uninvolved side). . Appley's Compression Test McMurrays Test . Lachman’s test. Lachman’s test is an alternative test assessing for laxity or rupture of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). This test is rarely required in an OSCE scenario, with the anterior drawer test being the preferred method of ACL assessment. 1. .
The Lachman test is the most accurate test for detecting ACL injury, followed by the anterior drawer . tellar compression, which will feel spongy if effusion is present. When hemarthrosis is . A positive Lachman test or pivot test is strong evidence of an existing anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear, and a negative Lachman test is fairly good evidence against that injury. Although . Lachman's test is used to diagnose ACL tears. 58.4 F. Chicago. Sunday, October 27, 2024 . Understanding the MRI of Cervical Nerve Compression; Understanding the MRI of Cervical Stenosis with Spinal Cord Injury; Thoracic. Understanding an .Importance of Test: The posterior cruciate ligament is responsible for resisting against excessive posterior translation of the tibia on the femur, due to its attachments on posteriorly on the tibial plateau and anteriorly on the lateral side of the medial femoral condyle (Neumann, 2010). A posterior translation force is applied to the proximal .
The Lachman test, unlike more complex diagnostic tools, requires minimal equipment and can be performed quickly in a clinical setting, making it an indispensable first step in the assessment of suspected ACL injuries.Its principal advantage lies in its ability to provide immediate insights into the ligament’s status, guiding further diagnostic and therapeutic .The ACL injury grades using the Lachman’s test are as follows.Grade 1 means 3-5 mm of translation, grade 2 is 5-10 mm of translation and grade 3 is greater than 10 mm of translation.In addition to assessing the amount of translation of the tibia and the quality of the end point of the Lachman test, it is also important to examine the patellar .Noble Compression Test/ Noble’s Test: PURPOSE: Tests for the presence of iliotibial band (ITB) friction syndrome, VIDEO DEMO, PROCEDURE, Positive Sign: Pain over the lateral femoral condyle at about 30° degrees of knee extension.
lachman test results results
Lachman test 3. Lateral pivot shift test 4. Posterior drawer test 5. Posterior sag sign 6. Slocum test 7. . Noble compression test 4. Patellar apprehension test. Anterior drawer test. Position patient in supine with knee flexed to 90 degrees and hip flexed to 45 degrees; .Definition/Description [edit | edit source]. The Noble’s test (Noble's Compression test) is a provocative test of the iliotibial band, developed by Clive Noble. It is commonly used as an indication for iliotibial band syndrome; however, no evidence-based research has been done yet to control the validity of this test.Other tests that could be used are the modified Ober’s test .LACHMAN'S TEST: Purpose: To test for the integrity of the Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL), VIDEO DEMO, PROCEDURE, Positive Sign: Pain or excessive anterior motion of the tibia, and disappearance of the infrapatellar tendon slope. . Apley’s Compression Test; Apley’s Distraction Test; Bragard’s Sign; Coronary Ligament Stress Test; Helfet .Lachman's test. Pivot shift test (MacIntosh test). Anterior drawer test for a ruptured anterior cruciate ligament. Have the supine patient flex his hips to about 45 degrees . Note that the opposite of the Apley distraction test is the Apley compression test. The patient assumes the same position, but the examiner applies a downward .
lachman test for knees
lachman test for acl
4 dias atrás · 处理器编号. E5-1620. 光刻. 32 nm. 建议客户价格. $294.00. CPU 规格. 内核数. 4. 线程数. 8. 最大睿频频率. 3.80 GHz. 英特尔® 睿频加速技术 2.0 频率‡. 3.80 GHz. 处理器基本频率. 3.60 GHz.
lachman compression test|lachman test for knees